- What is the NBU’s key policy rate?
- How the key policy rate affects everyone?
- Historical significance
- Comparison with other countries
- What is the double key policy rate of the NBU?
- Conclusions
The modern economy is a complex system in which every element matters. One of the most important indicators influencing the financial system of a country is the key policy rate of the National Bank of Ukraine (NBU). It plays a crucial role in regulating money circulation, controlling inflation, ensuring credit availability, and shaping the overall investment climate. Changes to this rate can significantly affect economic conditions for both businesses and individuals. Therefore, understanding how the key policy rate works helps assess financial situations more accurately and make informed decisions in personal and business finance.
What is the NBU’s key policy rate?
The key policy rate is the main interest rate set by the National Bank of Ukraine to implement the country’s monetary policy. It determines the minimum interest rate at which the NBU lends money to commercial banks or accepts their funds.
In simple terms, the key policy rate is a benchmark for the cost of money in the country. It shows what rate the NBU is willing to lend or borrow at. Commercial banks rely on this rate to set interest rates for loans and deposits for the public and businesses.
According to the Law of Ukraine “On the National Bank of Ukraine” the key policy rate is the main tool the NBU uses to regulate liquidity in the banking system and influence inflation, economic growth, and financial system stability.
The NBU sets the rate based on an analysis of macroeconomic indicators such as inflation levels and dynamics, exchange rates, and global economic trends. It follows a principle of predictability, announcing rate plans in advance to guide the market. If the market reacts too slowly, the NBU may use other instruments like liquidity management or increasing reserve requirements.
How the key policy rate affects everyone
The NBU’s key policy rate is one of the main tools used to regulate the pace of economic activity. The central bank may raise the rate to cool down inflation or lower it to stimulate growth.
A higher rate makes loans more expensive and less accessible, curbing demand and slowing down economic activity. However, it helps bring inflation under control and stabilize prices. For depositors, higher rates are a benefit as banks offer better returns, making saving more attractive.
A lower rate makes borrowing cheaper and more accessible. Businesses invest more, consumer spending grows, and the economy becomes more active. However, banks may lower deposit rates, making saving less attractive.
Thus, the key policy rate affects not only borrowing and saving costs but also the overall economic climate — growth rates, investment activity, consumer purchasing power, and price levels.
It’s worth noting that bank interest rates also depend on each bank’s own risk and interest rate policies, portfolio strategies, and liquidity levels. For example, after the March 2025 increase in the key policy rate by 1 percentage point, deposit rates in the top 20 banks rose by just 0.26–0.57 percentage points, depending on the term.
Influence of the NBU discount rate
| Rate Increase | Rate Decrease | |
|---|---|---|
| Loans | More expensive | Rate Decrease |
| Deposits | More profitable | Lower returns |
| Inflation | Slows down | Мay accelerate |
| Economic growth | Slows down | Stimulated |
Historical significance
Over the past decade, the key policy rate in Ukraine has changed many times. In 2015, due to crisis and 43% inflation, the rate was raised to a record-high 30%. From 2016 to 2019, it was gradually lowered, reaching 6% in 2020 to support the economy during the COVID-19 pandemic.
After Russia’s full-scale invasion in 2022, the NBU urgently raised the rate to 25% to contain inflation and stabilize the financial system. In 2023–2024, the rate was gradually lowered as inflation slowed and signs of recovery appeared. However, by the end of 2024, inflationary pressure returned due to rising consumer demand and hryvnia weakening. In response, the NBU raised the rate on December 13, 2024, to 13.5%.
In 2025, the NBU raised the rate further: to 14.5% on January 24 and to 15.5% on March 7. The goal was to maintain the attractiveness of hryvnia savings tools, protect the FX market, and keep inflation within targets.
On April 17, 2025, the National Bank decided to keep the key policy rate unchanged at 15.5% and does not plan to revise it in the coming months.
NBU key rate, schedule for 2015-2025
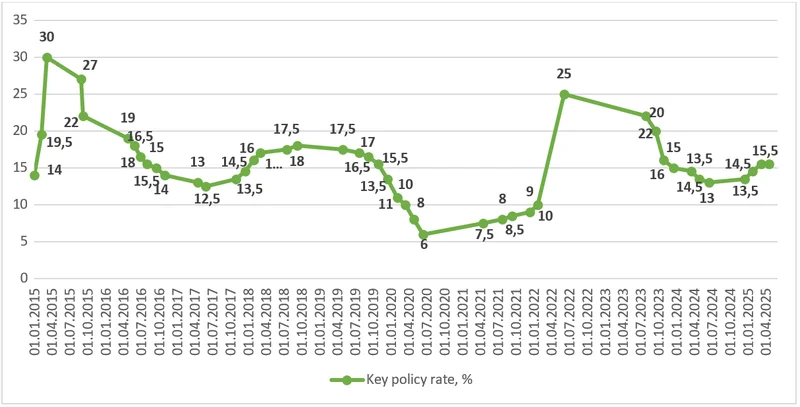
Data: National Bank of Ukraine
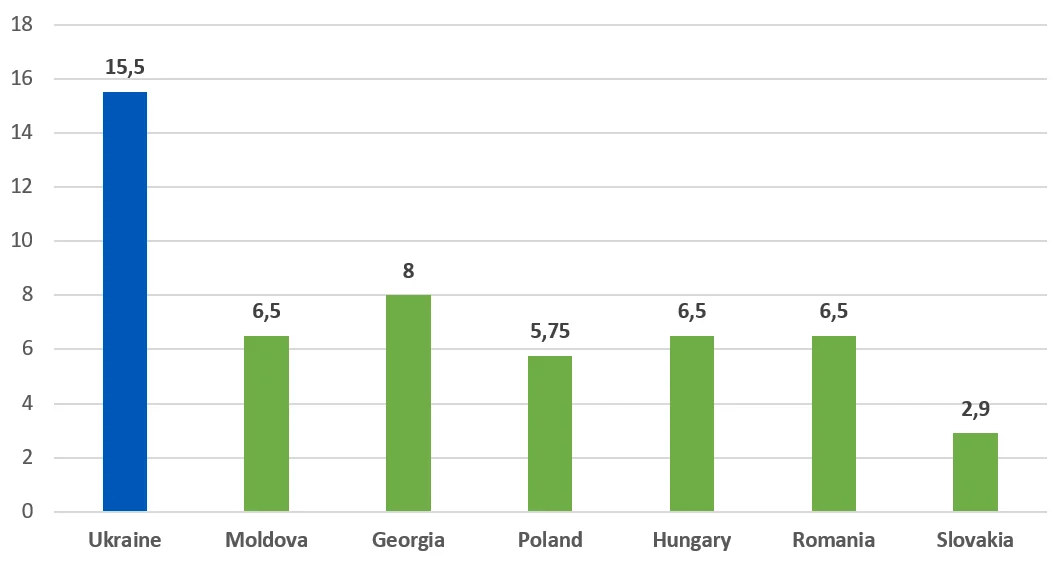
Comparison with other countries
As of April 7, 2025, the NBU’s key policy rate is 15.5% — relatively high compared to neighboring countries: Georgia — 8%, Poland — 5.75%, Slovakia — 2.90%, Hungary, Romania, and Moldova — 6.50%.
The discount rate of Ukraine and neighboring countries
What is the double key policy rate of the NBU?
The double key policy rate is a common benchmark used to calculate penalties for late fulfillment of contractual obligations — for instance, delayed payments or deliveries. It reflects the officially set rate and adjusts with changes to the NBU’s key policy rate.
According to Ukrainian law, the penalty (late fee) must not exceed double the NBU’s key policy rate effective during the delay period. Even if a contract states a higher penalty, the legal maximum applies.
Late payment penalty formula: Penalty = Debt amount × (Double NBU key rate / 100) × (Days overdue / 365)
Example: for a debt of UAH 10,000, NBU rate of 15%, and 30 days of delay: 10,000 × (15% × 2 / 100) × (30 / 365) ≈ 246.58 UAH.
Conclusions
The NBU key policy rate is a crucial instrument for regulating financial and economic policy. It has a significant impact on lending rates, inflation, the cost of money, access to financial resources, and overall economic development. A high key policy rate helps curb inflation, stabilize the national currency, and attract capital to the banking system, while a lower rate encourages business activity and stimulates consumer spending.
The NBU’s decisions on the key policy rate take into account a range of economic factors, including macroeconomic stability, global trends, and the level of domestic inflation. Proper management of the key policy rate enables effective responses to economic challenges and helps maintain the stability of the country’s financial system.
For businesses and individuals, it is important to monitor changes in the key policy rate, as it affects access to financial resources, deposit returns, and borrowing costs. Understanding what the National Bank of Ukraine’s key policy rate is and how it works makes it easier to plan financial activities and adapt to changes in the state’s monetary policy.